80. Remove Duplicates From Sorted Array II

Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove some duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears at most twice. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Custom Judge:
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
int[] nums = […]; // Input array
int[] expectedNums = […]; // The expected answer with correct length
int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
assert k == expectedNums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
}
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3]
Output: 5, nums = [1,1,2,2,3,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 1, 1, 2, 2 and 3 respectively. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,1,2,3,3]
Output: 7, nums = [0,0,1,1,2,3,3,,]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 7, with the first seven elements of nums being 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3 and 3 respectively.It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
原题链接: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/description/
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素最多出现两次,返回删除后数组的新长度。不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用O(1)额外空间的条件下完成删除操作。
示例 1
|
|
示例 2
|
|
这个问题怎么解决呢?
我们需要注意到的是:给定的数组是已经排好序的。可以确定的是需要一个变量i用于遍历数组,意思就是就算是比计算机聪明许多的人来处理这个问题,我们也要至少从左往右看一遍数组。还需要一个变量j用于存储删除重复出现元素后的数组长度(准确的说应该是长度减 1)。
初始情况下,i的值为2,j的值为1
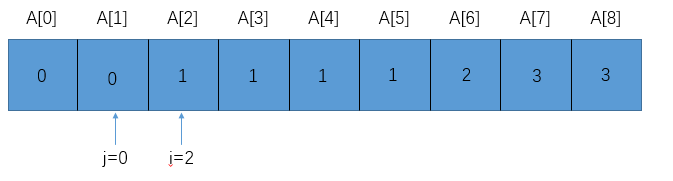
因为如果数组长度小于 3 的话,直接返回数组长度即可。
将重复元素按要求删除后,结果应该如下所示
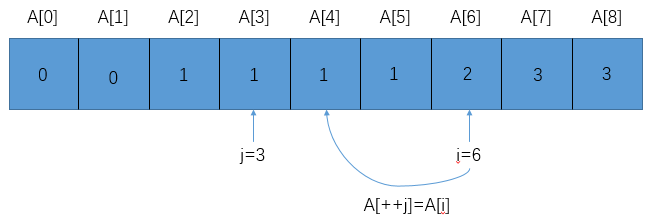
我们通过上图其实可以观察到,下标<=j的元素就是最终数组中该有的元素,而下标<i并且>j的元素就是那些重复的元素。下一步的操作就是A[++j]=A[i],然后i=i+1(以保持下标<=j的元素就是最终数组中该有的元素,而下标<i并且>j的元素就是那些重复的元素这个性质)。
什么时候会有A[++j]=A[i]这个操作呢?答案是A[j-1]!=A[i]时。由于我们的数组是有序的,对于合法的下标j-1,j,i,元素之间的关系应该是A[j-1]<=A[j]<=A[i]。如果A[j-1]==A[i]那么就意味着A[j-1]==A[j]==A[i],此时只需要i=i+1。如果A[j-1]!=A[i],这三个元素之间的情况可能有如下三种情况:
- 第一种
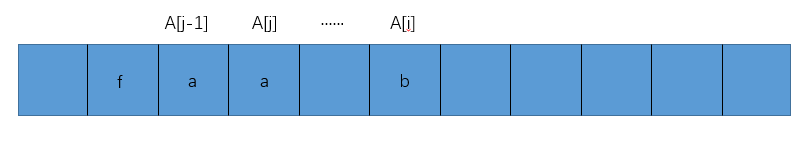
若出现上图所示的情况,我们可以推断出中间省略号部分其实省略的是a值(参考之前提到的性质),下一步的操作自然是A[++j]=A[i]。
- 第二种
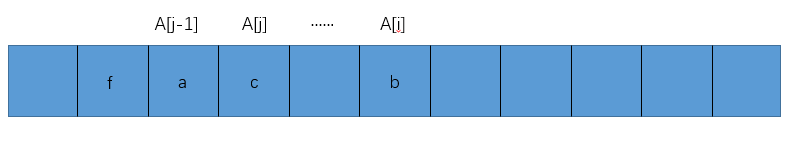
如果出现上图所示的情况,我们可以推断出省略号部分因应该是没有值的,也就是说j+1==i,此时A[++j]=A[i],也是没有问题的。
- 第三种
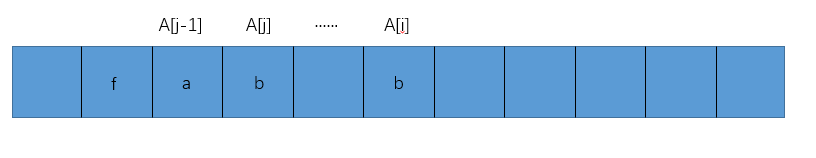
如果省略号部分省略是没有值的,那么下一步进行A[++j]=A[i]自然是没有问题的。如果省略号部分是有值的,那必定是已经移动到下标<=j保存下来的值,也就是说下标>j并且<i的元素都是处理好被弃用的值,此时进行A[++j]=A[i]也是没有问题的。
综上所述,当A[j-1]!=A[i]时,我们可以放心地进行A[++j]=A[i]这个操作。
接下来就可以实现上述思路:
|
|
相关内容
 支付宝
支付宝
 微信
微信