在日常 Node.js 开发中,你有没有遇到过这样一个错误:
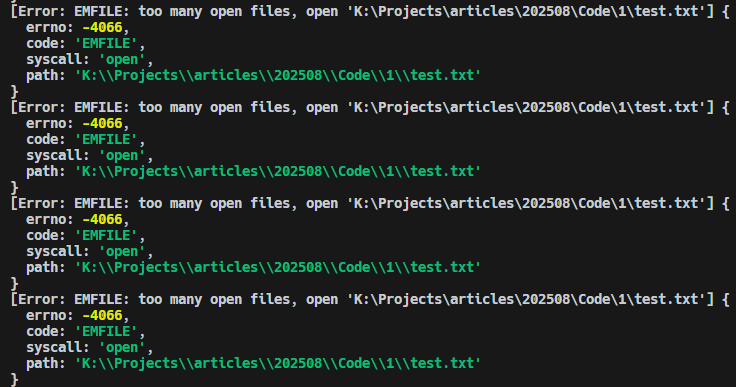
Error: EMFILE: too many open files
该错误通常出现在:批量文件操作、递归复制、日志处理等场景中。为什么会出现该错误?其实是因为在操作系统中每个进程最多可以同时打开一定数量的文件或 Socket, 而当打开的文件或 Socket 超过了这个限制时,就会出现“打开文件过多”的错误,导致程序突然崩溃。这种“打开文件过多”的问题看
似简单,但如果不加处理,尤其是在批量文件处理场景下,会让我们的 Node.js 程序非常脆弱。
错误示例
以下是一个简单示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import fs from 'fs';
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, 'test.txt');
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
fs.open(filePath, 'r', (err, fd) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log(`${i} 处理文件 ${filePath}`);
fs.close(fd, (err) => {
if (err) console.error(`关闭文件 ${filePath} 错误:`, err.code);
});
}
});
}
|
当我们node emfile.mjs运行这个脚本时,会出现EMFILE错误:
解决方案 1: 限制并发数
解决该错误的方法有很多。比如,我们可以限制每个进程同时打开的文件数量,或者限制单个文件打开的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
import fs from 'fs';
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, 'test.txt');
const MAX_CONCURRENT = 5;
const TIMES = 1000000;
let running = 0;
let index = 0;
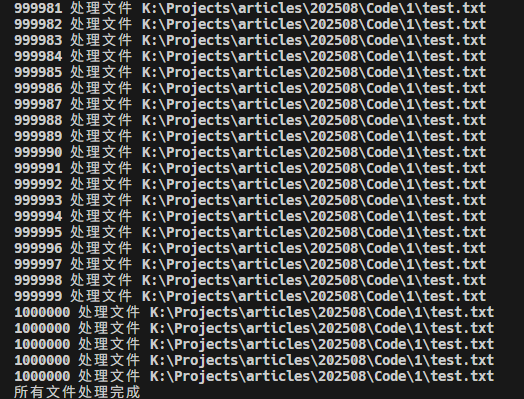
function processFile(filePath) {
if (index >= TIMES && running === 0) {
console.log('所有文件处理完成');
return;
}
while (running < MAX_CONCURRENT && index < TIMES) {
index++;
running++;
fs.open(filePath, 'r', (err, fd) => {
running--;
if (err) {
console.error(`打开文件 ${filePath} 错误:`, err.code);
} else {
console.log(`${index} 处理文件 ${filePath}`);
fs.close(fd, (err) => {
if (err) console.error(`关闭文件 ${filePath} 错误:`, err.code);
});
}
processFile(filePath);
});
}
}
processFile(filePath);
|
我们也可以选择三方库node-fs-extra解决这个问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
import fs from 'fs-extra';
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, 'test.txt');
async function processFile(filePath) {
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
try {
const fd = await fs.open(filePath, 'r');
console.log(`${i} 处理文件 ${filePath}`);
await fs.close(fd);
} catch (err) {
console.error(`文件 ${filePath} 错误:`, err.code);
}
}
console.log('所有文件处理完成');
}
processFile(filePath);
|
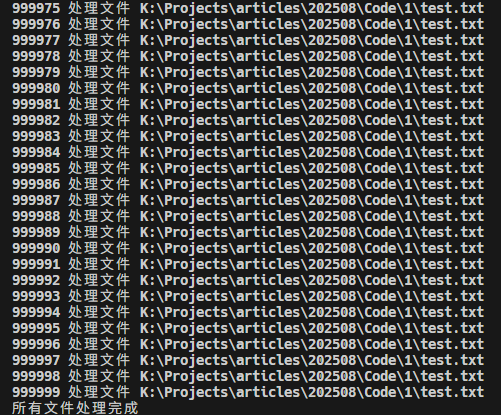
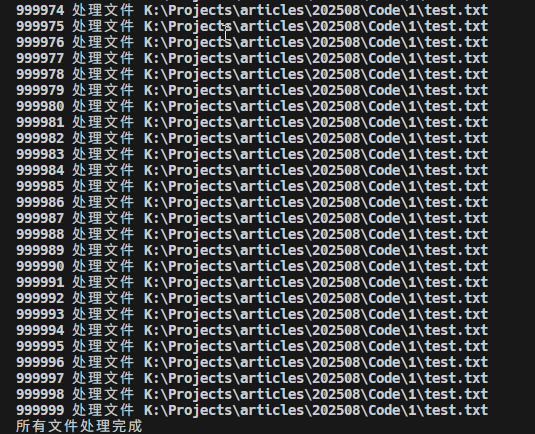
使用await fs.open和await fs.close 保证每个文件处理完就释放资源。上面的for循环是串行执行,天然避免一次性打开太多文件。如果想要提高效率,也可以用p-limit限制并发数,结合fs-extra更安全、高效。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import fs from 'fs-extra';
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
import pLimit from 'p-limit';
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, 'test.txt');
const TIMES = 1000000;
const MAX_CONCURRENT = 5;
const limit = pLimit(MAX_CONCURRENT);
async function processFile(filePath, index = 1) {
try {
const fd = await fs.open(filePath, 'r');
console.log(`${index} 处理文件 ${filePath}`);
await fs.close(fd);
} catch (err) {
console.error(`文件 ${filePath} 错误:`, err.code);
}
}
async function processFiles(filePath) {
const tasks = Array.from({ length: TIMES }, (_, index) =>
limit(() => processFile(filePath, index))
);
await Promise.all(tasks);
console.log('所有文件处理完成');
}
processFiles(filePath);
|
总结
Node.js 开发中,打开文件过多的问题是常见的,解决的方法也有很多。比如,限制并发数、使用三方库fs-extra等。在实际项目中,还需要根据具体场景选择合适的解决方案。





 支付宝
支付宝
 微信
微信